26 ループ量子重力理論 #重力 #宇宙
[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力]
・一般相対論と量子論を統合しようとする理論
・量子力学の原理に基づいて重力の力を説明しようとする量子重力理論の一つ。
26-1 概要 [1][2]
○時空(時間と空間)にはそれ以上の分割不可能な最小単位が存在する。
○この理論で時空は、結晶格子のように離散的な値をとるものと考えられている。このため、時空を連続的なものととらえたときに起きる短距離極限の発散が生じないという利点がある。
○粒子は種類ごとに、プランク定数という数を基本として、その回転数は飛び飛びの値を取っている。例えば電子は、プランク定数の1/2の速度で回転している。
<粒子のスピンの方向から、空間の方向を決める。>
・1950年代に、このスピンの原理を利用して、電子のスピンの方向から、空間の各点の方向を定義する「スピンネットワーク」理論が、ペンローズによって発表された。
・具体的な方法としては物質を点で表し、方向性を線で表して、その線に垂直な面で一定の体積を作る。
・そのサイズはプランク長(10^-35m)。
・これを空間の最小単位(量子)として、方向を表す線をなぞって一周する(ループを描く)と空間の方向の変化が分かる。
・この理論で時空は、点と線を使ってグラフで表される。このグラフはスピンネットワークと呼ばれる。
・このスピンネットワークの変化が重力や素粒子の存在を示していると考える。
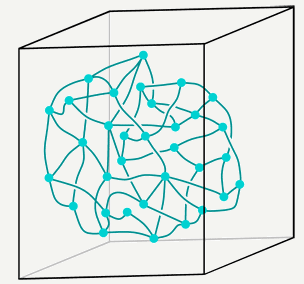
※スピンネットワーク[3]
<空間、重力、物質を一度に生み出し、表現できるのがループ量子重力理論の特徴>
・スピンネットワークに時間を加えたものをスピンフォームと呼ぶ。
・スピンフォームは時計の秒針が動くように離散的に変化する。
・変化前と変化後の時間の差は1プランク秒(10^-43秒)で、これが積もり積もって人が感じる時間となる。
・このようにループ量子重力理論では、時空は原子における電子配置のように離散的な値をとるものと考えられている。
26-2 超弦理論との相違
1)ループ量子重力理論と同じく量子重力理論の候補である超弦理論は、時空は背景場として最初からそこに存在するものとして定義しているが、ループ量子重力理論は、一般相対論と同様に理論自身が時空そのものを決定している。(背景独立性)
2)超弦理論では時空が10次元だが、ループ量子重力理論は、4次元。[4]
3)超弦理論ではすべての粒子が超対称性パートナーを有することになるが、ループ量子重力理論は超対称性を用いずに展開できる。[4]
4)ループ量子重力理論では、ビッグバンのような特異点は存在せず、宇宙の歴史は無限に遡ることができる。[3]
※インフレーションは量子重力効果によって引き起こされた。[5]・・・?
26-3 課題・今後の展開
○重力は自然界に存在する四つの力(基本相互作用)の中で最も弱く量子化された重力の観測が困難.。
○空間の構造が離散的だとすると,そこを伝わる光のスピードは波長によってわずかに異なる。はるか遠くの宇宙で発生したガンマ線バーストの光が,波長によってわずかな時間差をもって地球に届くことが検出されれば,理論を実証できる。[5] [6]
○2015年 カリフォルニア工科大とマサチューセッツ工科大などの共同研究チームが重力波を初検出。 [7]
○統一理論のようなもので科学を研究し尽くせない――フリーマン・ダイソンはその理由を、ゲーデルの不完全性定理で説明する。
【参考】
1. ループ量子重力理論 - Wikipedia
2. 教えて!goo
http://oshiete.goo.ne.jp/qa/1474170.html
3.Loop quantum gravity — Einstein Online
http://www.einstein-online.info/elementary/quantum/loops
4.リー・スモーリン ”時空の原子を追うループ量子重力理論”
http://www.nikkei-science.com/page/magazine/0404/loop.html
5.Carol Rovelli“Loop quantum gravity”
http://igpg.gravity.psu.edu/people/Ashtekar/articles/rovelli03.pdf
6.産経新聞 20160212
http://headlines.yahoo.co.jp/hl?a=20160212-00000502-san-sctch
7.No. 29 重力波
【更新履歴】
20170421 3項目に分割
20171030 今後の展開にフリーマン・ダイソンの言葉を追加。
25 M-Theory #MTheory #universe
[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+Strong interaction + Gravity]
1995 Edward Witten
○Hypothesis theory of 11-dimensional (spatial dimension is 10, one time dimension) comprehensive the five superstring theory that is currently known.
○In M-theory membrane of two-dimensional or 5-dimensional is considered as a component.
○While it is theoretically to be unified to represent the four force electromagnetic force, gravity, weak force, gravity in one form, this theory is the stage of mathematical hypothesis.
・・・We do not know how to quantize the membrane. Therefore, analysis of M theory is often done using eleven-dimensional supergravity theory which is low energy effective theory. [1]
○The M in M-theory can stand for "magic", "mystery", or "matrix" according to taste, and the true meaning of the title should be decided when a more fundamental formulation of the theory is known.
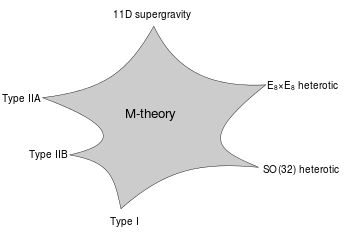
※A schematic illustration of the relationship between M-theory, the five superstring theories, and eleven-dimensional supergravity. [1]
○In this theory, only gravitational field (graviton field) , gravitino field and another field are available.
【参 照】
1. M-Theory – Wikipedia
【Change log】
2017-416 Add a schematic illustration
25 M理論 #M理論 #宇宙
[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力]
1995 Edward Witten
○現在知られている5つの超弦理論を総合する11次元(空間次元が10個、時間次元が1個)の仮説理論。
○2次元や5次元の膜が構成要素と考えられている。
○電磁気力、重力、弱い力、重力の四つの力を一つの形で表して統一しようとする理論であるが、数学的な仮説の段階。
・・・膜を量子化する方法が分かっていない。従って、M理論の解析は低エネルギー有効理論である超重力理論を用いて行われることが多い。[1]
○Mは、マジック(Magic)、ミステリー(Mystery)、メンブレーン(membrane;膜、超弦理論における「ひも」の構成要素)など、その人の好きなものを意味する。

※M理論、5つのスーパーストリング理論、および11次元超重力の関係の模式図 [2]
○この理論に登場する場は重力場(グラビトン場)・グラビティーノ場・3形式場のみ。[3]
【参 照】
1. 今村洋介”11次元超重力理論とMブレーン” 20110415
http://www.th.phys.titech.ac.jp/~imamura/note/m-kiso.pdf
2. M-theory - Wikipedia
3. M理論 - Wikipedia
【更新履歴】
20170416 模式図の追加
24 Superstring Theory:a Theory of Quantum Gravity #StringTheory #universe
[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+Strong interaction + Gravity]
○The phenomenon and force in the microscopic world is can be explained by the quantum theory, and macroscopic gravity phenomenon is can be explained by the general theory of relativity.
○Since 1980, scientists around the world are working on the development of the superstring theory that unifies general theory of relativity and the quantum theory, and that theory can be explained from the microscopic to the macroscopic world.
○Quantum theory has poor compatibility with gravity, would have obtained a result of the contradiction to be fitting the quantum theory to gravity. Superstring theory is expected as candidates for the theory that can be understood gravity in the framework of the quantum theory.
○For example, if the (early) size of the universe is as small as a point, the energy becomes infinite. The point of this energy infinity is the singularity.
○In the singularity the space-time disappears, and all of the physical law does not hold.
○If the particle is made of a string as shown by the string theory, the singularity does not come out.
○The superstring theory can handle gravity like the other three forces by representing the elementary particles as vibrations of the strings.
※In quantum scale, basic strings have become closed loope. Althoug the strings have various excited states, in one of such excited states, there is one with the nature of graviton(:particle that mediate gravity). [1]
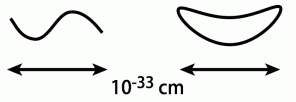
※Open string and closed string [2]
○In addition, the theory is possible to combine fermions and bosons together by thinking of super symmetry.
○However, considering that there is super-symmetry, it is necessary to assume the partner particles obtained by inverting particles and antiparticles, as a result, the number of particles are more than 100 kinds. Moreover, the space is a 10 dimensional.
※When trying to describe various particles uniformly, it becomes a theory of high dimension and supersymmetry. And with supersymmetry, there is only 11 –dimensional theory at maximum.
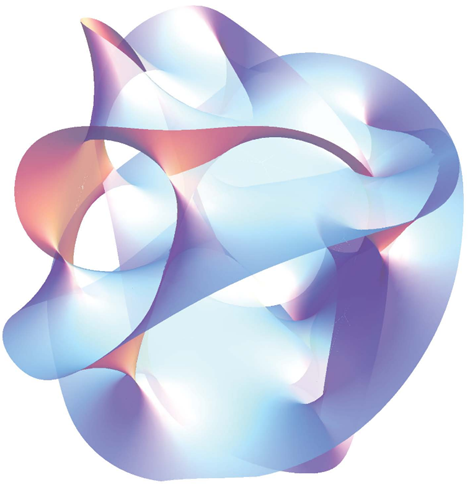
○Spatial dimension of 5-10(Extra Dimension:Calabi–Yau manifold) are folded into very fine "Planck distance" (10^-35 m) of magnitude. Various properties of elementary particles come out from there.
※Since there is no dimension of time in the extra 6-dimensional part of the string theory, the Euclidean space is bent and the gauge symmetry is naturally generated.
※Extra Dimension:Calabi–Yau manifold [3]
※Gauge symmetry: If there is a common physical law between the physical law of a certain world and the physical law of another world, a conversion rule of rulers is required. The fact that the physical law is established with this measure (gauge) conversion rule is called "gauge symmetry".
○By using string theory, we can calculate the entropy of black hole, Hawking radiation and so on. [4]
○Black hole entropy [5]
・Very heavy substances are required to make black holes.
・In string theory, D-brane is a good candidate.
・D-brane = a condensed one of strings
・Strings stick to D -brane .
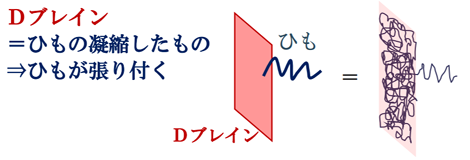
・Black hole=D –brane+Assembly of strings
・The number of string states matches the expected entropy.
○However from the size of a "string" which this theory assumes being very small(10^-35m) etc., the superstring theory has not acquired the status as an established theory of physics.
<Multiverse (Multi-Universe)>[1] [6][7]
・Superstring theory suggests that the Big Bang there was many times. In other words, the universe is not one. It will be that the universe is multi and there are parallel universes.
• In the parallel universe, the laws of physics are different, but superstring theory's seems applicable.
○Tasks
・There is no experimental evidence to date that confirms string theory's predictions of supersymmetry and Kaluza–Klein extra dimensions. [8]
• Verification of superstring theory by accelerator is not realistic. Superstring theory may be useful for clarifying black holes and dark matter.
【References】
1. A Universe from Nothing. Lawrence M. Krauss -2012
2. “超弦理論とブレーン世界”at ILCの物理(Japanese)
3. String theory - Wikipedia
4.Black hole thermodynamics - Wikipedia
5. 高柳 匡” 超ひも理論の最前線: 宇宙は量子ビットから 創られているのか?“20170524
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~tadashi.takayanagi/JAXA17.pdf
6.Michio Kaku / New York incandescent classroom "Dream of Einstein " 20150403
7. No.28-1-1 Superstring theory and Brane cosmology
8. Loop Quantum Gravity - Wikipedia
【Change log】
20170401 Addition of figure of strings
20170409 Addition of figure of Extra Dimension and Digression
20171229 Addition of Black hole entropy
24 超弦理論:量子重力理論 #超弦理論 #宇宙
[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力]
○ミクロの世界で働く力やそこで起こる現象は量子論で、巨視的な重力現象は一般相対性理論で説明できるようになっている。
○そして、1980年頃から世界中の科学者が量子論と一般相対性理論を統一して、ミクロから巨視的な世界までを説明できる超弦理論の開発に取り組んでいる。
○量子論は重力との相性が悪く、量子論を重力に対して当てはめると矛盾した結果が得られてしまう。
○例えば、(初期の)宇宙のサイズが点のように小さいとすると、そのエネルギーは無限大になる。この点のことを特異点という。
○特異点では時間も空間も消滅し、すべての物理法則が成り立たない。
○弦理論のように、素粒子は点ではなく、ひもでできていると考えると特異点が出てこない。
○超弦理論では、素粒子を弦の振動として表すことにより、重力を他の3つの力と同じように扱うことができる。また、超対称性によりフェルミオンとボソンを一つにまとめる(入れ換える)ことができる。
※超弦理論:超対称性を備えた(取り入れた)弦理論

※開いた弦と閉じた弦 [1]
○ただし、超対称性があると考えると、粒子と反粒子を反転したパートナー粒子を想定する必要があり、粒子の数は100種類を超える。また、空間の次元は10次元となる。
※様々な粒子を統一的に記述しようとすると、高次元かつ超対称性の理論となる。そして、超対称性を用いると、最高で11 次元の理論までしか存在しない。[3]
○弦理論の余分な6次元の部分(余剰次元:Calabi–Yau manifold)はきわめて微小な「プランク距離」(10^-35m)の大きさに畳み込まれている。そこから素粒子の色んな性質が出てくる。
※弦理論の余分な6次元の部分には時間の次元がないので、ユークリッド空間が曲がったような状況になっており、ゲージ対称性が自然に生成される。[4]
※余剰次元:Calabi–Yau manifold [5]

※ゲージ対称性:あるものさしの世界の物理法則と、別のものさしの世界の物理法則に共通の物理法則が存在する場合、ものさしの変換規則が必要となる。このものさし(ゲージ)変換規則をもって物理法則が成立することを「ゲージ対称性」と呼ぶ。
○弦理論を用いることで、ブラックホールのエントロピーやホーキング輻射等の計算ができる。[6]
○ブラックホールのエントロピー [7]
・ブラックホールを作るためには非常に重い物質が必要。
・弦理論ではDブレインが良い候補。

・ブラックホール=Dブレイン+ひもの集合体
・ひもの状態数は、予想されるエントロピーと一致する。
○しかし、この理論の想定する「ひも」の大きさが実証不可能に思えるほど小さい(10^-35m)ことなどから、超弦理論は物理学の定説としての地位を得るには至っていない。
<多元宇宙(マルチバース)> [8] [9][10]
・ひも理論では、6次元をどのようにコンパクト化するかによって、異なる物理法則、異なる力、異なる粒子を持ち、異なる対称性に支配された、異なる4次元宇宙が生じる。数学的には、ひとつの10次元ひも理論から、10^500種類もの4次元宇宙が予測される。
・4次元だけでなく、5次元、6次元、さらにもっと高い次元の宇宙さえ埋め込むことができる。
・つまり、宇宙は1つではなく多元であり、並行宇宙があるということになる。
○課題
・2013年4月のLHC実験では、超対称または4次元以上の次元の証拠を見つけることができなかった。[11]
・加速器による超弦理論の検証は現実的ではない。超弦理論は、ブラックホールや暗黒物質の解明に役立つ可能性がある。
【参 照】
1. “超弦理論とブレーン世界”at ILCの物理
http://www-jlc.kek.jp/ilcphys/hep_intro/brane
2. 川合光“究極の理論「超ひも理論」を完成させる”at RIKEN NEWS 200605
http://www.riken.jp/~/media/riken/pr/publications/news/2006/rn200605.pdf
3.今村洋介”11次元超重力理論とMブレーン” 20110415
http://www.th.phys.titech.ac.jp/~imamura/note/m-kiso.pdf
4. 江口 徹“理論で「ひも」解く宇宙”at 東京大学理学部大学院HP
https://www.s.u-tokyo.ac.jp/ja/story/newsletter/labo/10.html
5. String theory - Wikipedia
6.杉本茂樹 ”超弦理論の魅力”
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~shigeki.sugimoto/YITP50.pdf
7.高柳 匡” 超ひも理論の最前線: 宇宙は量子ビットから 創られているのか?“20170524
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~tadashi.takayanagi/JAXA17.pdf
8.「宇宙が始まる前には何があったのか?」ローレンス・クラウス(2013年11月刊)
9.Michio Kaku / New York incandescent classroom "Dream of Einstein " 20150403
10. No.28-1-1 超弦理論とブレーン(薄膜)宇宙モデル
11. Loop Quantum Gravity - Wikipedia
【更新履歴】
20170401 弦の図の添付
20170409 余剰次元の図と余談の追加
20171229 ブラックホールのエントロピーの追加
23 Higgs field and Higgs Boson #higgs #universe
23-1 Higgs field and mass
○The Higgs field is an energy field that is thought to exist everywhere in the universe. [1]
○In Higgs field, particles(except photon, require energy of mc ^ 2 additionally. [2] So they now cannot travel at the speed of light. [1]
※If the energy of the interaction between certain particle and Higgs field is strong, the mass of the particle increases. (It will require significant energy to move the particle) [2]
○Higgs field condensed by the time the temperature of the universe fell, then mass and the Higgs boson appeared. [3]
:The birth of mass( After 10^-9 second The temperature of the universe 10^13K)
※If the Higgs field did not exist, particles would not have the mass required to attract one another, and would float around freely at light speed. [1]
○However, Higgs field is the original of 2% of mass. [4]
※Most of the mass of protons and neutrons is the kinetic energy of elemental particles (quark, antiquark, gluons). [5]
※Energy also has mass according to the principle of mass–energy equivalence.
○There are two types of mass. [6]
1) Difficulty of acceleration → inertial mass ••• by Higgs field
2) Degree of weight due to gravitation → gravitational mass ••• by gravitational field
1) and 2) are equivalent.
※The equality of inertial and active gravitational mass remains as puzzling as ever.
23-2 Higgs boson
○Higgs boson is the vibration of the Higgs field. : Higgs boson appears when you excite the Higgs field.
・Spin, Electric charge:0 [4]
・Mass:125.3 GeV [4]
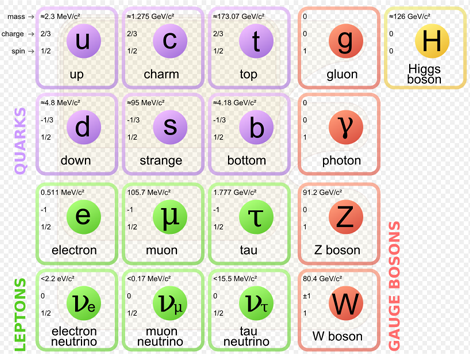
※The Standard Model of elementary particles (more schematic depiction), with the three generations of matter, gauge bosons in the fourth column, and the Higgs boson in the fifth.
MissMJ - Own work by uploader, PBS NOVA, Fermilab, Office of Science, United States Department of Energy, Particle Data Group [7]
※ Graviton does not enter into the standard model. Gravity can not be described well with the Standard Model.
○July 04, 2012, Conseil Europeenne pour la Reaherche Nucleaire (CERN, in Switzerland)announced that they discovered a new particle which they could believe it as Higgs boson. [1]
○April 2015 Restart of LHC operation: There is a theory that predicts that there are five types of Higgs particles, so verification of its correctness is a problem.
※LHC:The Large Hadron Collider Iis the world's largest and most powerful particle collider, most complex experimental facility ever built, and the largest single machine in the world. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) .It lies beneath the France–Switzerland border near Geneva, Switzerland. [8]
【References】
1. Higgs field - Wikipedia
2. ヒッグス粒子と質量の謎(ヒッグス粒子は何をするのか)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/timeandspace2014/lec14_higgs.html
3. 島根大学集中講義 真空の性質2009
http://osksn2.hep.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/~naga/kogi/shimane-class09/shimanelec2_vac.pdf
4. Higgs boson - Wikipedia
5. ヒッグス粒子にはできないこと-物理学と切手収集
http://d.hatena.ne.jp/hundun2/20111219/1324367739
6. Mass - Wikipedia
7. Standard Model - Wikipedia
8. Large Hadron Collider - Wikipedia
23 ヒッグス場とヒッグス粒子 #ヒッグス #宇宙
23-1 ヒッグス場と質量
○ヒッグス場は宇宙全体に広がるエネルギー場。
○ヒッグス場では、光子・グルーオン・重力子を除く粒子はmc^2のエネルギーを余分に必要とする。[1] その結果、光速で移動できなくなる。[2]
※ある粒子と、ヒッグス場との相互作用のエネルギーが強い場合、その粒子は質量が大きくなる(粒子を移動させるのに大きなエネルギーが必要になる)。[1]
○宇宙の温度が下がるとヒッグス場が凝縮し、質量とヒッグス粒子が現れた。[3]
:質量の誕生 (10^-9秒後 宇宙の温度:10^13K)
※質量がなかったら、素粒子は光速で飛び回るだけで、物質は生まれなかった。
○ただし、ヒッグス場により生じる質量は質量の2%。[4]
:陽子や中性子の質量の大部分は素粒子(クォーク、反クォーク、グルーオン)の運動エネルギー。[5]
※エネルギーは質量とエネルギーの等価性の原理により、質量を持つ。
○質量には2種類ある。[6]
1)加速の与えにくさ→慣性質量 (inertial mass)・・・ヒッグス場による
2)万有引力による重さの度合い→重力質量 (gravitational mass)・・・重力場による
1)と2)は等価。
※なぜ慣性質量と重力質量が同じ値をとるのかという理由は判っていない。
23-2 ヒッグス粒子
○ヒッグス粒子はヒッグス場の振動。:ヒッグス場を励起するとヒッグス粒子が現れる。
・ヒッグス粒子は電荷とスピンを持たない。[4]
・ヒッグス粒子の質量は125.3 GeV。[4]
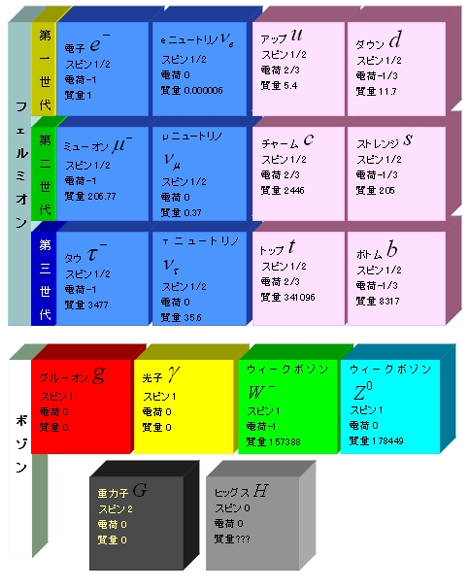
※標準模型 [7]
※グラビトン(重力子)は標準模型の中には入らない。標準模型では重力はうまく記述できない。
○2012年7月4日 欧州合同原子核研究所(CERN、スイス)は、ヒッグス粒子と見られる新粒子を発見したと発表した。[4]
○2015年4月 LHC運転再開: ヒッグス粒子が5種類あると予言する理論もあるので、その正否の検証が課題になる。
※LHC:大型ハドロン衝突型加速器Large Hadron Collider) 高エネルギー物理実験を目的としてCERNが建設した世界最大の衝突型円型加速器。スイス・ジュネーブ郊外にフランスとの国境をまたいで設置されている。
【参 照】
1.ヒッグス粒子と質量の謎(ヒッグス粒子は何をするのか)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/timeandspace2014/lec14_higgs.html
2. Higgs field - Wikipedia
3.島根大学集中講義 真空の性質2009
http://osksn2.hep.sci.osaka-u.ac.jp/~naga/kogi/shimane-class09/shimanelec2_vac.pdf
4. ヒッグス粒子 - Wikipedia
5. ヒッグス粒子にはできないこと-物理学と切手収集
http://d.hatena.ne.jp/hundun2/20111219/1324367739
6. 質量 - Wikipedia
7.CatFalcon“この世界は単純だ”
http://blogs.yahoo.co.jp/cat_falcon/22535344.html
22 Quantum Field Theory #universe #quantum
22-1 What is Quantum Field?
○Space is quantum fields, particle is the excited quantum field.
※Vacuum (nothing condition) is the quantum fields where the energy is the lowest.
○In quantum field theory, we consider particles(Material fields)as harmonic oscillators and quantize them. Then, as a system of infinite number of harmonic oscillators, the theory is assembled.
※The motion of an object that is connected to a spring and vibrates is called "harmonic oscillation".
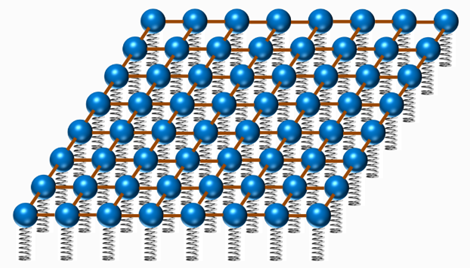
※Image of Quantum field [1]
○Quantum field theory combines special relativity theory and quantum mechanics.
・・・The difference between special and general relativity is gravity only. In the world of elementary particles, since the mass is small, the work of gravity is equivalent to almost completely nothing compared to other forces.
○Quantum mechanics is an approximate form of quantum field theory limited to the low energy state.
・Quantum mechanics can not be used for phenomena in which the number of particles changes such as particle generation and extinction.
○Prior to the emergence of string theory, the theory describing the smallest scale was quantum field theory.
22-2 Field types and particles
1)Gauge field and gauge particle (force mediating particle)
Electromagnetic field ・・・Photon
Weak interaction (causing β decay of neutrons) • • • W boson, Z boson
Strong interaction(Power to combine quarks)・・・Gluon
Gravitational field・・・Graviton
※ Gauge theory(3 + 1 dimension) is the theory underlying the Standard Model.
※As a method to describe gravity, there is a method based on Newton's theory of gravity and general relativity.
※The state with the lowest energy of the string is the gauge particle. ← Superstring Theory
2)Material field and material particles

※Under the "quarks and leptons" definition, the elementary and composite particles made of the quarks (in purple) and leptons (in green) would be matter—while the gauge bosons (in red) would not be matter. However, interaction energy inherent to composite particles (for example, gluons involved in neutrons and protons) contribute to the mass of ordinary matter. [2]
3)Higgs field (scalar field) and Higgs particle
22-3 その他
○Quantum field theory is the fundamental theory of particle physics (describing behavior of elementary particles), nuclear physics, condensed matter physics (describing multi-body theory effects such as critical phenomena and phase transitions).
【References】
1. Brian Skinner”A Children’s Picture-book Introduction to Quantum Field Theory” 20150820
http://www.ribbonfarm.com/2015/08/20/qft/
2.Matter - Wikipedia
22 場の量子論 #宇宙 #量子論
22-1 場とは?
○空間は場であり、粒子は場が励起されたもの。
※真空(何もない状態)とは、最もエネルギーが低い状態の場。
○場の量子論では、粒子(物質場)を調和振動子と考えて量子化する。そして、無限個の調和振動子の系として,理論が組み立てられる。
※バネにつながれて振動する物体の運動を「調和振動」と呼ぶ。

※場のイメージ[1]
○場の量子論は、特殊相対性理論と量子力学を組み合わせたもの。
・・・特殊と一般相対性理論の違いは重力のあるなしだけ。素粒子の世界では質量が小さいこともあり、重力の働きは他の力に比べてほぼ完全に無いに等しい。[2]
○量子力学は、場の量子論を低エネルギー状態に限った時の近似形 [3]
・量子力学は、粒子の生成・消滅等、粒子数の変化する現象に対しては使えない。[4]
○超弦理論が登場する以前に最も小さなスケールを記述した理論は場の量子論だった。
22-2 場の種類と粒子 [5]
1)ゲージ場とゲージ粒子(力を媒介する粒子)・・・ボソン
電磁場・・・光子
弱い力(中性子のβ崩壊を起こす力)・・・Wボソン、Zボソン
強い力(クォークを結びつける力)・・・グルーオン
重力場・・・重力子(グラビトン)
※ゲージ場を扱うゲージ理論(3+1次元)は標準理論の基礎。
※重力場:重力を記述する手法としては、ニュートンの重力理論と一般相対性理論に基づく手法がある。[7]
※弦の一番エネルギーの低い状態がゲージ粒子。←超弦理論
2)物質場と物質粒子
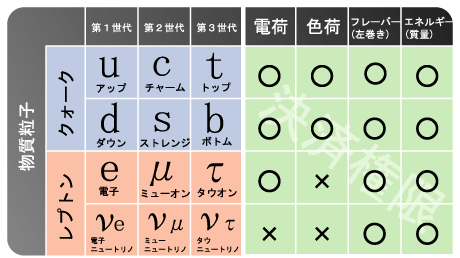
※物質粒子[8]
3)ヒッグス場(スカラー場)とヒッグス粒子・・・ボソン

※標準モデル [9]
22-3 その他
○場の量子論は、素粒子論(素粒子の振る舞いを記述)・原子核物理学・物性論(臨界現象・相転移などの多体論的効果を記述)の基礎理論。[3]
○場の量子論は数学的に定式化されていない。[10]
○量子論と一般相対性理論を統合する理論が必要。[10]
【参 考】
1. Brian Skinner”A Children’s Picture-book Introduction to Quantum Field Theory” 20150820
http://www.ribbonfarm.com/2015/08/20/qft/
2. EMANの物理学・素粒子論・場の理論/やっぱり初めはラグランジアン
http://eman-physics.net/elementary/lagrangian.html
3.場の量子論 - Wikipedia
4. 場の量子論 20130718
http://kscalar.kj.yamagata-u.ac.jp/~endo/kougi/QFT/QFT2013.pdf
5.ヒッグス粒子と質量の謎(ヒッグス粒子は何をするのか)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/timeandspace2014/lec14_higgs.html
6.重力場 - Wikipedia
7. active_galactic
http://d.hatena.ne.jp/active_galactic/20081029/1225217750
8. Higgs boson - Wikipedia
9.大栗博司”宇宙の数学とは何か“200907
21 Quantum Cosmology #universe #cosmology
21-1 The Birth of the universe:Quantum fluctuation [1] [2]
・In modern physics, there is no such thing as perfect nothing.
・Vacuum or empty space has Vacuum energy and tension.
・In quantum level, even in a vacuum, pairs of matter and anti-matter particles are constantly being created and annihilated.
・The universe was born by the rapid expansion of the quantum fluctuation.

※Vacuum fluctuations [3]
※The problem remains.・・・ What is the vacuum energy?
21-2 Inflation cosmology [4]
・・・1981 Katsuhiko Sato, Alan Guth
・The theory is that the universe is the magnitude of 10^24-th power(=Inflation) in the period from after 10 minus 36 square seconds immediately after birth until after 10 minus 34 square seconds by the phase transition of space due to the Quantum tunneling of vacuum energy.
※The size of the universe (10^-27m) is much smaller than atom (10^-10m).
⇒3 millimeters (10^-3m)
※The inflation rate is 60-fold of light speed.
○The driving force behind this inflation has been said that the energy that was released during the phase transition of the vacuum. [5]
○In early inflationary models, the phase transition of the vacuum was considered that it is generated by the Quantum tunnelling or tunnel effect. However, in a model named new inflation or slow-roll inflation, instead of tunneling out of a false vacuum state, inflation is considered that occurred by rolling down a potential energy hill. [5]
※Quantum tunnelling or tunneling refers to the quantum mechanical phenomenon where a particle tunnels through a barrier that it classicallycould not surmount. It has important applications to modern devices such as the tunnel diode,[2] quantum computing, and the scanning tunnelling microscope. [6]
※Nuclear fusion is also thanks to the tunnel effect. Without the tunnel effect the sun can not shine. [7]
・Huge energy is converted into heat. And it will be the whole universe to the ultra high. ⇒ Big Bang
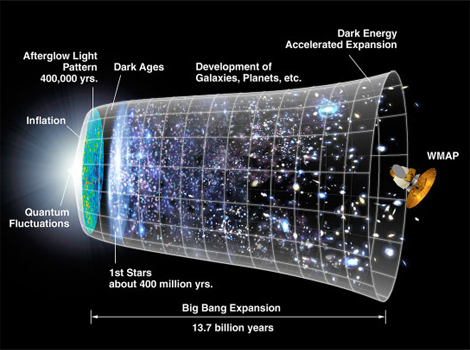
• By inflation, some of the problems of big bang cosmology, which has been pointed out in the 1970s is resolved. [4]
(The problems of big bang cosmology )
1-That the universe is observed is very flat. (Flatness problem)
2 -The universe is extremely uniform. (Horizon problem)
3-Phase defect of space in which exist in many models of grand unified theory (GUT) has been predicted is not observed at all. (Monopole problem)
<Problems and observation>
・Driving force of the secondary inflation that began before several billion years (4 ~ 6 billion years) remains as unresolved issues. [8]
・Precision exploration of gravity waves is planned by such as Planck(cosmic microwave background radiation observation satellites of the European Space Agency (ESA) ) or the South Pole satellite. [8]
・In February 2016, the Advanced LIGO team announced that they had detected gravitational waves from a pair of black holes merging. [9]
・Institute for Cosmic Ray Research, University of Tokyo starts the observation of gravitational waves in 2017 by the underground telescope "KAGRA".
・In the 2021 fiscal year, Japan plans to launch the artificial satellite "Light Bird" which is possible all-sky observation with high degree accuracy.
21-3 Free lunch model(Alan Harvey Guth)[8]
・・・1988
・Matter and radiation can have not only "positive" energy but also "negative" energy.
・Negative energy is repulsive force, and repulsive force inflates the space.
・When "negative" energy is generated by quantum fluctuations, "positive" energy of the same amount is also generated.
• Thus, in the closed universe, material and radiation is filled accoding to the expansion!
・This is perfectly consistent with the Law of Conservation of Energy, so the Expansion of the universe is the ultimate Free lunch.
・Guth’s model is believed to explain the cosmological constant of General relativity.
21-4 The Big Bang model [10]
・・・1948 George Gamow
The model is assumed that the Universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state.
・The Big Bang model is explained by Cosmology based on theory of elementary particles.
・Elementary particles are explained by several kinds of symmetry in theory of elementary particles.
・Although it is assumed that there is an equivalent amount of matter and antimatter in the universe from this, there is not much antimatter to be found. Something must have happened to tip the balance.
・One of the greatest challenges in physics is to figure out matter and antimatter asymmetry.
☆My idea
Since the fundamental power of antimatter is repulsive force, it is thought that antimatter was diffused at high speed rather than the substance after separation of gravity and antigravity (10E-44(ten to the minus 44th) second after the Big Bang).
【References】
1. No.16 Uncertainty Principle
2. Jeff Miller, Ph.D.” Can Quantum Mechanics Produce a Universe from Nothing?”
http://www.apologeticspress.org/apcontent.aspx?category=12&article=4584
3. RevoScience”Young researcher proposes new explaination for unsolved problems in physics…”
http://revoscience.com/en/young-researcher-proposes-new-explaination-for-unsolved-problems-in-physics-and-revolutionizes-the-theory-of-quantum-fluctuations/
4. Wikipedia:Inflation(cosmology)
5. No.16-3 Phase Transitions of Vacuum /Inflation Cosmology/Quantum Tunneling
6. Wikipedia:Quantum tunnelling
7. Masahiro Maeno “Introduction to Quantum mechanics(Japanese) " 20060216 (p.107)
http://www.phys.u-ryukyu.ac.jp/~maeno/qm/qm.pdf
8.A Universe from Nothing. Lawrence M. Krauss -2012
9. Wikipedia:Gravitational wave
10. No.18 The Big Bang model