What Is Aperture In Photography: Everything You Need To Know
Attempt photographing the same scene with different apertures. Figure out the maximum worth for your lens that offers you the sharpest, highest-quality image. If you wish to blur the background more or to make all the objects in the frame sharper, just make certain you increase or reduce the shutter speed value by a number of notches from the optimal value.
Effortlessly Understanding Aperture
Lots of photographers are familiar with the golden triad of direct exposure settlement: shutter speed, ISO, and electronic camera aperture. Together, these three are the artist's very first line of defense when operating in the field. While the shutter speed determines how long the entrance student of the lens remains open, aperture is a measure of how commonly the hole is held during this period of time.
In the front of any lens, there is a hole called the electronic camera aperture. It is utilized to manage how much light is allowed into the electronic camera. Fanning blades dilate as the artist opens it, and close as the artist shuts it. The broader you hold the aperture open, the more light falls through, and vice versa.
What Is Aperture? A Photographer's Complete Guide
As the aperture closes, the slice handles volume and can enrobe a subject of measurement completely, bringing the whole individual or object into focus simultaneously. The size of the aperture should be among the very first things to consider when composing the image around whatever you wish to remain in focus.
A tight aperture will produce a razor-sharp image, and this impact continues to some level, even as you move outward from the heart of the focal plane. No lens is capable of keeping everything in front of it in best focus at the same time, not even one with the narrowest aperture possible.
Everything You Need To Know About Aperture In Photography
When you would like every information to ring loud, clear, and true, shooting with a smaller aperture is a safe bet in the exact same method that a low ISO and a fast shutter speed will likewise safeguard you from marring the image in the heat of the moment. At the other end of things, a bigger lens aperture will result in a somewhat softer, more diffuse look.
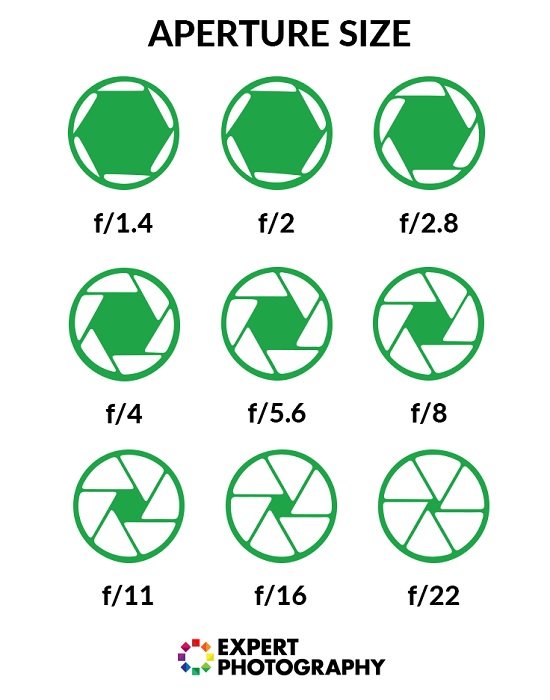
This number, called an f-stop, is used to break down the series of possible diameters so that an increase of one f-stop will always either double the amount of light being let into the video camera or suffice exactly in half. The exact same factor to consider is taken with shutter speed and ISO, such as when increasing one's ISO from ISO 800 to ISO 1600.
Aperture - Everything You Need To Know
This offers a common language for all three of these various elements to be handled in. The scale of f-stops is not absolutely universal, but some typical ones consist of f/1.2, f/1.4, f/2, f/2.8, f/4, f/5.6, f/8, f/11, f/16, f/22, f/32, and f/64. F/4 is regarded by numerous as the sweet spot for a variety of practical kinds of photography.
Among the benefits of operating in a studio setting is having total control over how it is configured. Inside your home, even something like a 1K fresnel or an inexpensive strobe will be adequate to support an extremely narrow aperture. Definition and integrity are easy to accomplish when working this way.
Ultimate Guide To The Camera Aperture And Depth Of Field
When shooting something big like a mountain at daybreak, there generally is no requirement to separate the majesty of the topic from the background. Lots of choose to see the entire scene in crystal-clear focus. A narrow aperture is far more efficient in seeing whatever in front of it at the same time.
While not constantly the method to go, it actually is easy on the eyes when done well and at the correct time. Let's discuss when you need to utilize a large aperture. When light is limited, broad aperture photography supplies the artist with the ways of producing an adequately exposed image under a variety of conditions.
Here's What You Need To Know About Aperture
A shallow depth of field imitates a spotlight that lets them shine. When shooting for yourself, there are no guidelines. Follow the subject's lead and you will seldom be led astray. If your gut is telling you to go large, we recommend that you beware. The right aperture to choose? One might say that it's already best in front of you.
.
What Is Aperture?
The aperture system in the lens that allows more or less light to come in is formed of a series of nontransparent "blades". When the blades are open, your camera sensing unit will capture more light, whereas as the blades progressively close, less light will strike your sensor. In a similar method to our eyes, considering that it works like the human pupils: the larger they are, the more light will pass through and vice versa.
Big apertures are also referred to as fast apertures considering that they enable you to decrease the exposure time, and small apertures are also referred to as sluggish apertures, given that they enable you to increase the shutter speed. Depending upon what you desire to capture, there are particular situations where you shouldn't alter your ISO and shutter speed; aperture will be the key to an appropriate exposure.
Here's What You Need To Know About Aperture
According to the physics laws in optics, you'll have the ability to capture, implying more areas of your images will be out of focus and less sharp. Conversely, you'll see in your image, indicating a larger proportion of the image will be in focus.
The same thing takes place when you set a small aperture. Because case, there is a phenomenon related to aperture in photography which is an optical impact that leads to poorer quality throughout the image. You can see this phenomenon as you begin closing the aperture above f/16 values.
Aperture In Photography: All You Need To Know
To compute this sweet spot, approximately move 2 to 3 F-stop values from the maximum aperture of your lens. For example, if the maximum aperture in your lens is f/4, this would be in between f/8 and f/11/.
Before digital photography, the aperture was by hand set on the lens by choosing the specific F-value. This changed in digital electronic cameras today. There are still some manual lenses that need you to set the aperture by hand, however all the electronic lenses that work with your digital cam will allow you to quickly select your aperture.
Everything You Need To Know About Aperture
Beyond all the that we've currently seen, there are other intriguing side effects of utilizing various apertures in some light situations. To/sunburst or a moonstar, you'll need to have high F-Stop values from f/16 to the smallest aperture on your lens. That way, the sun/moon beams will be sharper. This also depends upon the variety of blades on the aperture of your lens.
What Is Aperture?
What is aperture in photography and how does it impact the method our photo looks? Aperture is the most essential pillar of the exposure triangle after shutter speed and ISO, so it's vital you comprehend it! Terms like f-stops and depth of field may frighten beginner professional photographers, but they're actually not that complicated.
Smaller sized aperture = darker picture. EASY! Utilizing the aperture to control the quantity of light that comes through your lens is sometimes an imaginative option you make. Other times you may be required to select a particular aperture based on the readily available light you have in your scene.