In the dynmamic landscape of modern-day service, Six Sigma stands apart as a beacon of efficiency and quality. This data-driven, customer-focused technique is changing companies worldwide, leading them towards exceptional levels of functional excellence. Established by The Motorala Co
In the Nineteen Eighties, Six Sigma has because ended up being a basic method in various markets, intending to improve procedures, reduce waste, and make the most of customer fulfillment.
Six Sigma is a variety of methods and tools for procedure enhancement, based on the concept of lowering irregularity in procedures. It seeks to enhance the quality of output by determining and getting rid of the reasons for defects and minimizing irregularity in production and organization procedures. Six Sigma employs a variety of quality management techniques, stats and allows the production of group of specialists in an organisation who specialise in these techniques.
Its main focus is on quality assurance. By rigorously examining every element of the production procedure, it assists in determining and getting rid of the sources of problems. This method not only guarantees a premium end product however also fosters a culture of continuous enhancement.
By improving procedures and decreasing mistakes, Six Sigma considerably lowers costs associated with rework, waste, and unacceptable consumer experiences. Companies employing Six Sigma methods have reported significant savings, highlighting its efficiency in enhancing monetary performance.
The customer-centric method of Six Sigma ensures that the service or products are customized to fulfill, and typically surpass, consumer expectations. This results in greater client complete satisfaction, loyalty, and, subsequently, a boost in repeat organization and referrals.
Six Sigma methods improve processes, getting rid of unneeded steps and optimizing workflow. This performance not just accelerates the production cycle however likewise maximizes workers to focus on more value-added activities, hence increasing overall productivity.
At its core, Six Sigma has to do with making choices based on information and analytical analysis, rather than presumptions. This unbiased approach causes more reliable problem-solving and tactical planning, aiding companies in navigating intricate obstacles.
Implementing Six Sigma includes training employees in its methodologies, empowering them to identify and resolve issues. This not just develops a knowledgeable workforce but also boosts staff member engagement and ownership of procedures.
Six Sigma leads to the standardization of procedures, making it simpler to reproduce success and maintain consistency throughout different operations of a service. This uniformity is especially important for business operating on an international scale.
By identifying possible issues before they end up being problems, Six Sigma assists in mitigating dangers. It offers an organized method to foreseeing and handling possible failures, enhancing the general stability of service operations.
Under the leadership of leading executive, Mister Welch, General Electric Inc executed Six Sigma in Nineteen Ninety Five and reported billions of dollars in savings over the following years. It became a part of the company's culture, driving effectiveness and development.
As the pioneer of Six Sigma, Inc utilized this approach to substantially lower its manufacturing defects, setting a brand-new standard for quality. The company conserved an estimated $14 billion in the 1980s and 1990s.
Carrying Out Six Sigma in the early 2000s, Inc used these principles to streamline processes and enhance quality, leading to significant savings and a robust turn-around in their service performance.
In spite of its numerous advantages, implementing Six Sigma is not without obstacles. It needs a considerable investment in training and a cultural shift towards data-driven decision-making. Furthermore, the extensive nature of Six Sigma can in some cases be viewed as inflexible, requiring careful balance and adaptation in dynamic service environments.
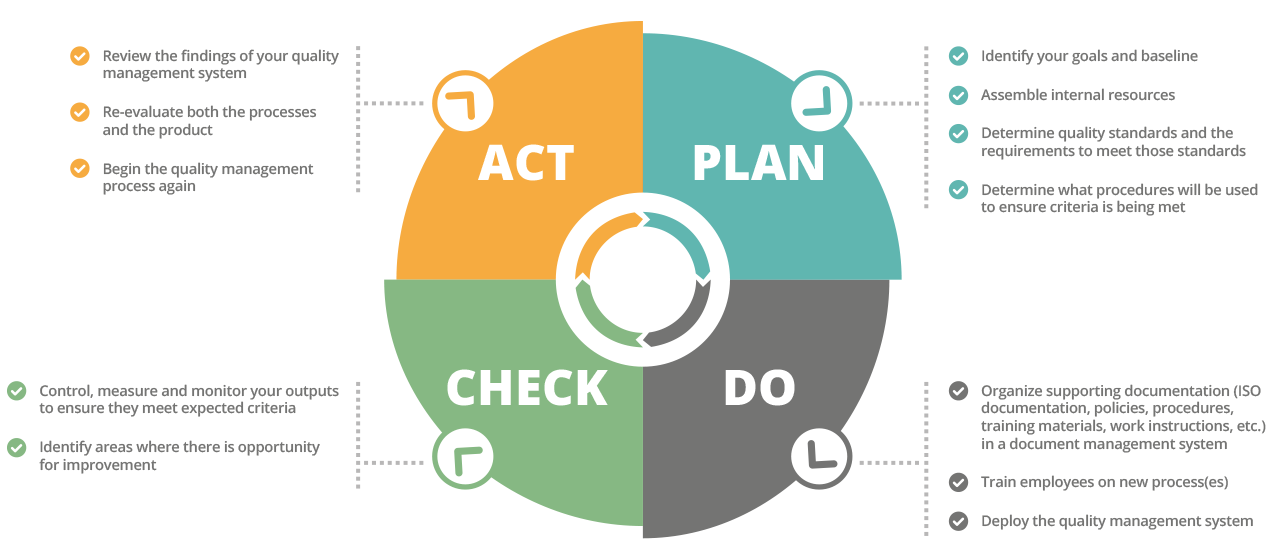
In a time where precision and consistency are the cornerstones of making quality, Statistical Process Control (SPC) stands apart as a vital tool. Rooted in data and information analysis, SPC supplies producers with a scientific approach to make sure quality and effectiveness in their procedures. By keeping an eye on and managing production processes, SPC enables makers to accomplish and preserve premium standards, essential in today's competitive market.
SPC is quality assurance technique which uses statistical strategies to control and keep track of procedures. It is an aid to ensuring that the procedures run effectively, producing more specification-conforming products with much minimized waste of materials. SPC can be adjusted for use with any systems or process where the "conforming item" output can be measured. Key tools utilized in SPC consist of control charts, process capability analysis, and Style of Experiments.
Control charts, the heart of SPC, are charts used to study how a process modifications with time. They outline information in time order and help distinguish between regular procedure variation and variation due to unique causes. By determining these variations, manufacturers can take corrective actions immediately before they result in malfunctioning products.
In automobile production, SPC helps in keeping tight tolerances in engine parts production. Control charts keep track of aspects like the diameter of pistons or the thickness of brake pads, guaranteeing each part fulfills rigid quality standards.
In the pharmaceutical industry, SPC is used to monitor tablet weights or the purity of ingredients, ensuring that every batch of medication is safe and efficient for customers.
The food and drink industry utilizes SPC to keep an eye on temperatures, pH levels, and other crucial aspects to make sure product consistency and security.
SPC allows for early detection of problems, decreasing the event of problems and making sure premium output. By minimizing waste and remodel, SPC assists producers cut expenses significantly. SPC enhances processes by recognizing ineffectiveness, resulting in much faster production times and higher throughput.
SPC offers a quantitative basis for decision-making, causing more effective and effective management of making procedures. Top quality, constant products result in greater customer fulfillment and commitment.
While the advantages of SPC are clear, its implementation is not without difficulties. It requires a considerable investment in training and technology. Additionally, a culture shift towards data-driven decision-making is essential for SPC to be effective. Resistance from employees, absence of management support, and inadequate understanding of analytical techniques can also pose considerable barriers.
With developments in innovation, the scope of SPC is expanding. The integration of SPC with digital innovations like IoT (Web of Things) and AI (Synthetic Intelligence) is opening new frontiers. Real-time data collection and analysis are ending up being more advanced, allowing a lot more exact control over manufacturing processes.
Statistical Process Control is more than a set of tools; it is a viewpoint of continuous enhancement and commitment to quality. In the landscape of modern-day manufacturing, where quality and performance are not simply preferred but required, SPC stands as a pillar of operational quality. As markets continue to evolve, the principles and practices of SPC will unquestionably continue to play a crucial function in shaping the future of production.
In the today's busy business environment, organizations are constantly looking for methods to stay ahead of the curve. Business Process Re-engineering (BPR) has actually emerged as a pivotal technique for business looking to significantly improve their operations, increase efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction. BPR involves reassessing and redesigning organization procedures to accomplish dramatic enhancements in critical performance procedures, such as expense, quality, service, and speed.
Business Process Re-engineering is not about making ISO 9001 accreditation cost incremental improvements or tweaks to existing processes; it has to do with essentially rethinking how work is done to achieve a considerable leap in efficiency. This approach requires a thorough analysis of the business's core processes and systems, challenging the existing norms and assumptions.
The very first action in Business Process Re-engineering is acknowledging the need for modification. This could be due to numerous factors such as declining efficiency, client discontentment, or the introduction of brand-new technologies. Clearly define what the BPR efforts aim to attain. Set specific, quantifiable objectives and figure out the scope of the procedure to be re-engineered.
Not all procedures are appropriate for re-engineering. Choose procedures that are critical to the service and have the potential for significant enhancement. Draw up the existing procedure in detail. Understand the workflow, inputs, outputs, and the functions of different stakeholders. This understanding forms the basis for redesign.
This is the core of BPR. Upgrade the process to achieve the set objectives. This might involve getting rid of unnecessary steps, lowering complexities, automating tasks, or completely reimagining the procedure flow. Develop a service case that lays out the advantages, costs, and dangers related to the re-engineered procedure. This will help in protecting buy-in from stakeholders.
Put the brand-new process into action. This stage requires careful preparation, resource allowance, and alter management