36 意識とは? #知性
36-1 概 要
○意識とは、自分の今ある状態や、周囲の状況などの環境を評価できている状態のこと。
・ ぼんやりした意識は犬・猫などにもある。
○意識の単位・・・ サーモスタットを1単位とすると、[1]
花 10単位
動物 数百単位
○意識のレベル [1]
レベル1:空間を認識できる。(は虫類)
レベル2:空間と社会を認識できる。(ほ乳類)
レベル3:空間、社会、時間を認識できる。(人間)
※さらに、満足を先延ばしにできる能力が成功できるかどうかの差になる。

36-2 自己意識(self-consciousness)=自己認識=自意識
:自分自身に向けられる意識
○私的自己意識と公的自己意識[2]
・私的自己意識:自己の内面(感覚,感情,思考など)に向けられる。(前帯状皮質(anterior cingulate cortex, BA32)、内側前頭前野(medial prefrontal cortex, BA10)、後帯状皮質(posterior cingulate cortex, BA 23/31)、および楔前部(precuneus, BA7)を含む大脳皮質正中内側部構造(cortical midline structure))
・公的自己意識:他者が観察できる自己の外面(容姿や振る舞い方など)に向けられる。(脳の前頭頭頂領域)
○自己意識の存在を調べるテスト[2]:
対象の額に鮮やかなマークを塗り、次に、鏡の前に対象を置く。対象が自分の額のマークに触れようとした場合、自己意識の存在を示す証拠と考える。
・ヒトでは、2歳前後まで開発されない。[2]
・動物の中でもチンパンジーやオランウータンなどの大型類人猿、ゾウやイルカなどにはあるが、サルには無いとされている。[2]
・自己意識がなければ嫉妬も無い。

36-3 ベイジアンネット [3]
○AIのベイジアンネットは自分自身を認識する能力を持ち得る。
・ただし、「意識」という言葉は様々な意味で使われることがあるので 注意が必要。
・意識の非機能的な側面は、ベイジアンネットでは再現できない。
※ベイジアンネット:確率論に基づいた推論を効率的に行うための技術。 脳の機能の1つである直観と似た働きをする。脳の情報処理原理の解明の鍵となる技術。
・イギリスの牧師トーマス・ベイズ(1702年(?) - 1761年)によって1763年に発見されたベイズの定理をもとにしている。
36-4 量子脳理論
イギリスの数学者、宇宙物理学・理論物理学者ロジャー・ペンローズ(Roger Penrose, 1931- )は、著書『皇帝の新しい心』にて、脳内の情報処理には量子力学が深く関わっているという仮説を提示している。
素粒子にはそれぞれ意識の元となる基本的で単純な未知の属性が付随しており、脳内の神経細胞にある微小管で、波動関数が収縮すると、その未知の属性も同時に組み合わさり、生物の高レベルな意識が生起するというのである。
※ペンローズは微小管が神経伝達に関わっていると考えていたようだが、微小管( microtubule)は、細胞骨格の一種。
神経伝達は神経細胞においては膜電位の変化(アクションポテンシャル)の伝播により、神経細胞間では化学物質を介して行われる。
※ホーキングは、「仮にOR(Objective-Reduction、客観的収縮:波動関数の発展と収縮に関する仮説理論)を認めたにしても、(余りに微細なことがらなので)現実に脳の仕組みやシステムがそれに影響を受けるとは考えがたい。」としている。
36-5 量子コンピュータ [4][5][6]
素粒子は0と1というように、2つの状態(ビット)を同時にもつ(重ね合わせの状態)性質がある。
この性質をコントロールすると、少ないビットで多くの状態を表すことができる。これによって、今までは一つずつ処理していた計算を、同時に(並列的に)処理し、現在のスーパーコンピュータで数千年かかっても解けないような計算でも数十秒で解くことができる。
2011年(128) D-Wave Systems社(カナダ)が量子コンピュータ「D-Wave」の建造に成功した。
☆意識が素粒子の属性に起因するものであるならば、量子コンピュータの進歩に伴い、AIも意識を持つ可能性がある!=非生命体知性との出会い!
36-6 人工意識(Artificial Consciousness、AC)
・人工知能に自己意識を与えることは倫理的な問題がある。
・自己意識を持つ者に対してはその個性を認め共存する必要がある。
・自己意識を持つ者を隷属させようとすれば必ず反乱を生む。
【参 考】
1.「最新物理学が語る驚異の未来」ミチオ・カク(2015年4月)
Eテレ ニューヨーク白熱教室 20150424 意識と心
You Tube:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-dMt5FB6inY
※加來 道雄、Michio Kaku、1947年1月24日 –
ミチオ・カク公式サイト
2. 脳科学辞典/自己意識/守田知代
http://bsd.neuroinf.jp/wiki/%E8%87%AA%E5%B7%B1%E6%84%8F%E8%AD%98
3.産業技術総合研究所 > 一杉裕志 > 脳とベイジアンネット > 脳とベイジアンネットFAQ( 2011-05-26 更新)
4.No.40 成長する人工知能(GAI)
5. 量子コンピュータ - Wikipedia
6.日経ビジネス/世界初「量子コンピューター」生みの親、「訂正」に挑む/西森秀稔へのインタビュー
http://business.nikkeibp.co.jp/atcl/report/15/215171/091400001/?rss&rt=nocnt
35 What is Intelligence? #Intelligence
○Intelligence is the capability of a language and a network.
Etymologically it is the capability of the selection accompanied by consciousness.
※ Origin of the word: Originate in a Latin verb "intellegere" and mean the ability of "legere(choose)" from "inter(between)" two or more choices. However, the instinct beforehand programmed by the gene is not intellect. Intellect is the acquired capability to create the possibility of new selection.
Reference:"System methodology archive" (~2011) Toshiya Nagai
http://www.systemicsarchive.com/ja/a/intellect.html
※ In Goo Dictionary, intellectus is the capability which gets to know things and considers and judges.Capability to perform man's intellectual action.
○Dolphin, Chimpanzee, and the Orangutan can recognize themselves.
→Since there are communications skills, it is not as man, but it can be said that it has intellectus.

○The main feature of intellectus is creative!
☆Level of intelligence
Level1 Frontal lobe of the brain to judge and create.
Level2 Brain is using artificial intelligence to auxiliary. (The current)
Level3 Brain and artificial intelligence do judgment and creativity together.
35 知性とは? #知性
○知性は言語及びネットワークの能力。語源的には、意識を伴った選択の能力。
※語源:ラテン語の動詞“intellegere”に由来し、複数の選択肢の“間から inter”“選ぶlegere”能力を意味する。ただし、選択の能力といっても、遺伝子にあらかじめプログラムされた本能は知性でない。知性は新しい選択の可能性を切り開く後天的な能力。
参照:「システム論アーカイブ」(~2011年)永井俊哉
http://www.systemicsarchive.com/ja/a/intellect.html
※goo辞書では、物事を知り、考え、判断する能力。人間の、知的作用を営む能力。
○イルカやチンパンジー、オランウータンは私を認識できる。
→コミュニケーション能力があることから、人間ほどではないが、知性を持つと言える。

○創造することは知性の最大特徴。
☆知性のレベル
レベル1 脳の前頭葉が判断・創造している。
レベル2 脳が人工知能を補助的に使っている。(現在)
レベル3 脳と人工知能が一体となって判断・創造している。
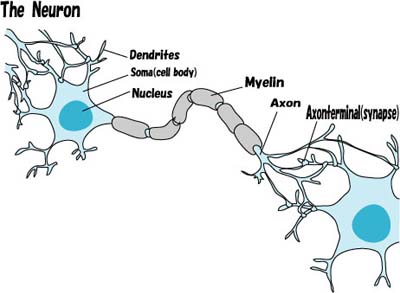
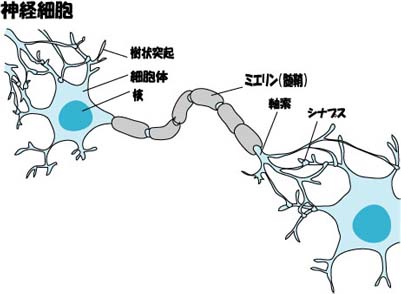
34 Cell and DNA(DeoxyriboNucleic Acid) #Intelligence
○Cell
・Humans are made of about 100 trillion cells.
・The human nervous system is estimated to consist of roughly 360 billion non-neural glial cells and 100 billion nerve cells.
・Incidentally, the birth of multicellular organisms is the Cambrian about 600 million years ago.
○DNA(DeoxyriboNucleic Acid)
・Every person has about 25,000 different genes.
・Plant is an animal of seniors with 40,000 or more genes.
※Gene: The corresponding DNA sequence to a protein.
・The length of human DNA in a single cell is 1.8 meters. (2 nanometers wide)
※1nanometer is one point nine times ten to the minus second.
・The length of the blood vessels in the adult is about 100,000 km(1×10E5m).
※Earth's diameter is 12,700 km(1.27×10E4m).
・The world largest is 62-th power of 10 of the world smallest.
・DNA of human and chimpanzee is consistent 98.5 percent.
○World of Living thing
・The Biological World is made by the coincidences and an accumulation of trial and error of over 100 millions years. This was not inevitable. Susumu Tonegawa "Spirit and Matter"
34 細胞とDNA #知性
○細胞
・人間は約100兆個の細胞でできている。
・脳の神経細胞は大脳で数百億個、小脳で1000億個、脳全体では千数百億個。
・ちなみに、多細胞生物が誕生したのは約6億年前のカンブリア紀。
○DNA(DeoxyriboNucleic Acid)
・ヒトは、約25,000個の遺伝子を持つ。
・動物の先輩である植物は、40,000個以上の遺伝子を持つ。
※遺伝子:実在が確かめられているタンパク質に対応するDNA配列。
(参 照)「遺伝子の数え方」福岡 伸一
http://www.sotokoto.net/jp/essay/?id=26
・人間のひとつの細胞中のDNAの長さは1.8メートル。(幅2ナノメートル)
※1ナノメートルは、10-9メートル
・成人の血管の長さは約10万キロメートル(1×105m)。
※地球の直径は12,700キロメートル(1.27×104m)。
・一番大きい世界は、一番小さい世界の10の62乗倍
・人間とチンパンジーのDNAは98.5%一致している。
○生物の世界
・生物の世界というのは、何億年にもわたる偶然の積み重ね、試行錯誤の積み重ねでいまこうなっているということであって、こうなった必然性なんてない。 利根川進「精神と物質」
33 Mathematics #Universe
○Mathematics is the alphabet with which God has written the Universe. -Galileo Galilei (1564 - 1642)
○How can it be that mathematics, being after all a product of human thought which is independent of experience, is so admirably appropriate to the objects of reality? —Albert Einstein
○Key word:Symmetry [1]
※Forecast of mathematics:Those that do not can still prove.
(It is well in the world of mathematics.)

【Mathematical history】
About 7000 years ago Number was born. (Mankind began to group living.)
16th century Imaginary number is accepted.
・・・"Forgetting the mental anguish received with imaginary number, and merely introducing this." Gerolamo Cardano(Italy 1501~1576)
17th century Minus is accepted in Europe.
・・・Descartes draws a number line. René Descartes(France 1596~1650)
The first half of the 19th century An imaginary number is denoted by an axis of coordinates.:complex plane Carolus Fridericus Gauss(Germany 1777~1855)
1935 Gödel's Incompleteness Theorem
・・・Then, Turing(Aan Mathison Turing, UK 1912-1954) proved that there is no unific method of confirming beforehand whether a certain proposition is a proposition which cannot judge truth.
1964 Murray Gell-Mann (1929-)predicted the existence of quarks by the theory of pure mathematics(the group:SU (3)).
【References】
1. Relationship between mathematics and physics - Wikipedia
2.Edward Vladimirovich Frenkel(1968-)
http://www.nhk.or.jp/hakunetsu/math/
【Change log】
20170416 Addition of a photo
20170419 Addition of the words of Einstein
33 数学 #宇宙
○数学は神が宇宙を書いたアルファベットだ。-ガリレオ・ガリレイ
○経験とは独立した思考の産物である数学が,物理的実在である対象と,これほどうまく合致しうるのはなぜなのか? -アインシュタイン
○キーワード:対称性 [1]
※予想:まだ証明できていないもの。(数学の世界ではよくある。)

【数学の歴史】
約7000年前 数字が誕生した。(人類が集団生活を始めた。)
16世紀 虚数を認める
・・・「虚数によって受ける精神的苦痛は忘れ、ただこれを導入せよ」カルダノ(イタリア 1501~76)
17世紀 ヨーロッパでマイナスが認められる・・・デカルトが数直線を描く
デカルト(仏 1596~1650)
19世紀前半 座標軸で虚数を現す:複素平面 ガウス(独1777~1855)
1931年 不完全性定理 ゲーデル(オーストリア 1906-78)
・・・その後、チューリングが、ある命題が真偽を判定できない命題であるかどうかを、あらかじめチェックする統一的な方法がないということを証明した。
1964年 マレー・ゲルマン(1929-)は純粋数学の理論(群:SU(3))を使ってクォークの存在を予言した。
【参 考】
1. NHK 数学ミステリー白熱教室 エドワード・フレンケル(1968-)
http://www.nhk.or.jp/hakunetsu/math/
【更新履歴】
20170416 写真の追加
20170419 アインシュタインの言葉の追加
32 What is the Universe?+The History of Cosmology #Cosmology
32-1 What is known
1)Macro phenomena such as celestial movements and evolution of the universe can be explained by general relativity.
2)Using quantum mechanics describing the micro world, we can explain the three powers of "electromagnetic force" "strong interaction" "weak interaction".・・・Standard theory, Higgs boson etc.
3)The unification of general relativity and quantum mechanics is yet to be seen.
⇒The universe is expanding, but we can not see the future at the present moment.
32-2 Hawking's question
Q:Why does the universe exist in spite of trouble?
Q:Can a unified theory of the universe explain the universe accurately?
Q:Or we need the Creator?
Q:If so, the Creator gives the effect of something else in the universe?
Q:And who created the Creator?
Source: "Brief History of Time" Stephen William Hawking (issued April 15, 1995)
32-3 Freeman Dyson's words
○We can not fully study science with something like a unified theory - Freeman Dyson explains the reason with Gödel's incompleteness theorems

☆Image of the Universe
【The history of cosmology】
1895 William James(1842-1910) coined the term Multi-Universe(Multiverse).
1900 Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck(1858 -1947) advocated that the light, X-rays and other electromagnetic waves were released as a constant mass that he called quantum.
1905 Special relativity[1]・・・Theory of electromagnetism that Albert Einstein(1879-1955) announced.
1913 Bohr's model(Niels Henrik David Bohr(1885-1962))・・・A pioneer of quantum mechanics (Old quantum theory).
・Electron is a wave.
・The length of the electrons orbit around the nucleus is an integer multiple of the electron wavelength (10 minus 10 square m).
(Bohr, de Broglie)
1915-1916 General theory of relativity(General relativity)(Einstein) [1] [Electromagnetic force + gravity]
・Einstein explained that the gravity caused by the mass distort the space-time.
• When written in Newtonian mechanics[2] the phenomenon of error increases (movement in the near to the speed of light or large gravitational field) can be correctly described.
• In general relativity, spacetime is expected never to stay inflated or deflated steady or the black hole[3] is expected to forme when a large mass to concentrate on limited space.
・Einstein predicted the existence of gravitational waves[4] in 1916 in his general theory of relativity.
1920s Quantum mechanics
・Atomic, electronic and electromagnetic waves have the characteristics of the particles and waves.
1922 Friedman found the expanding universe solutions in general relativity equations.
1925 Pauli exclusion principle
1926 Werner Heisenberg was put together the uncertainty principle[5].
※Uncertainty principle:It is a characteristic of the system, such as the wave. In knowing pair of physical properties (eg position and momentum) at the same time, there is a fundamental limit of accuracy.
1928 Dirac theory
・Either both consistent:theory of quantum mechanics and special relativity
・There is positron(antimatter) that is the partner of electron.
1929 Discovery of cosmic expansion(the redshift)(Edwin Powell Hubble)
1932 Discovery of positron(antimatter)
1934 Fritz Zwicky coined the term dark matter. [6]
1948 -Big Bang model [7]
-Quantum electrodynamics, QED [Electromagnetic force ]
• Electromagnetic interaction acting between charged particles, including electrons is caused by the transfer of particles called photons.
1957 Bryce Seligman DeWitt (1923–2004) coined the term many-worlds interpretation; MWI.
1960 Freeman Dyson advocated Dyson Ball
1964
・Peter Ware Higgs proposed the theory of generation of mass. [8]
・Cosmic microwave background (radiation)(; CMB、CMBR)[7]discovered.
1968 Weinberg-Salam theory[9] [Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction]
1970 Penrose and Hawkins (co-authored paper)
・On the basis of the general relativity theory, they were finally prove that should there was a big bang singularity in the very early universe.
• In the singularity, the effect of small scale of quantum mechanics dealing can not be ignored.
• However, if you take into account the quantum effect, singularities disappear. ...?
1970s
・Only one force was present in the beginning of the universe, then, the force was divided into electromagnetic force, weak interaction, strong interaction and gravity, so physicists are trying to expresse these four forces in one form.
-Standard Model, SM [Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction(+ Strong interaction)] [9]
-Grand unification theory or Grand unified theory、GUT[Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+ Strong interaction] [10]
The late 1970s -Quantum chromodynamics [9]
1980s Cosmology based on theory of elementary particles[10]
1981 Cosmic inflation Theory [11]
1984 Superstring Theory [12] [Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+Strong interaction + Gravity]
1986~ Loop Quantum Gravity [13]
1995 M-theory[14] [Electromagnetic force + Weak interaction+Strong interaction + Gravity]
1998 -Michael S. Turner coined the term dark energy. [6]
-Observed the accelerated expansion of the universe(Brian P. Schmidt)
2016 Studio Gooda! coined structure of dark matter. [7]
【References】
1. No. 14 Theory of Relativity
2. No. 13 Newtonian Mechanics
3. No. 80 Black Hole
4. No.31 Gravitational Wave
5. No.16 Uncertainty Principle
6. No.9 Dark Matter and Dark Energy
7. No.18 The Big Bang Mmodel
8. No. 23 Higgs Field/Higgs Boson
9. No.19 Standard Theory(Standard Model)
10. No.21 Quantum Cosmology
11. No.21-2 Inflation cosmology
12. No.24 Superstring Theory
13. No.26 Loop Quantum Gravity
14. No.25 M-theory
15. No.84-4-2 A Structure of Dark Matter
【Change log】
20170416 Addition of the image of the Universe
20170515 Addition of No.32-1 What is known
20171030 Addition of No.32-3 Freeman Dyson's words
32 宇宙とは?+宇宙論の歴史 #宇宙論
32-1 分かっていること
1)天体の動きや宇宙の進化などマクロな現象は一般相対性理論で説明できる。
2)ミクロの世界を記述する量子力学を用いて、「電磁気力」「強い力」「弱い力」の3つの力を説明できる。・・・標準理論、ヒッグス粒子 等
3)一般相対性理論と量子力学の統一の行方は見えない。
⇒宇宙は膨張しているが、現時点でその未来を見通すことはできない。
32-2 ホーキングの疑問
Q:宇宙はなぜ、存在するという面倒なことをするのか?
Q:統一理論には自分自身の存在をもたらすほど大きな強制力があるのか?
Q:それとも創造主が必要なのか?
Q:もしそうだとすれば、創造主は宇宙に何か他の影響も与えるのではなかろうか?
Q:そして、創造主を創造したのはだれなのか?
出典:「ホーキング宇宙を語る」スティーブン・W・ホーキング(1995年4月15日発行)
(p.239)
32-3 フリーマン・ダイソンの言葉
○統一理論のようなもので科学を研究し尽くせない――フリーマン・ダイソンはその理由を、ゲーデルの不完全性定理で説明する。

☆宇宙のイメージ
【宇宙論の歴史】
1895年 ウィリアム・ジェームズ 多元宇宙という言葉を作る。
1900年 マックス・プランク(1858 -1947) は、光、X線その他の電磁波は、量子と彼
が呼んだ一定のかたまりとして放出されると唱えた。
1905年 特殊相対性理論 [1]:アルベルト・アインシュタイン(1879-1955)が発表した電磁気学の理論。[電磁気力]
1913年 ボーアの原子模型(ニールス・ボーア(1885-1962)):電子は波で、原子核を回る軌道の長さは波長(10のマイナス10乗m)の整数倍(ボーア、ド・ブロイ)
1915-1916年 一般相対性理論 [1] [電磁気力+重力]
・質量が時空間を歪ませることによって、重力が生じることを説明した。
・ニュートン力学[2]で記述すると誤差が大きくなる現象(光速度に近い運動や、大きな重力場における運動)を正しく記述できる。
・時空は膨張または収縮し、定常にとどまることがないこと、限られた空間に大きな質量が集中すると、光さえ脱出できないブラックホール[3]が形成されることを予測した。
・重力波[4]の存在を予測。
1920年代 量子力学
・原子・電子・電磁波は粒子としての特徴をもつと同時に波としての特徴をもつ。
1922 年 フリードマンが一般相対論方程式の中に膨張宇宙解を見つけた。
1925年 パウリの排他原理
1926年 ヴェルナー・ハイゼンベルグが、不確定性原理[5]をまとめあげた。
※不確定性原理:波のような系に備わっている特性。一対の物理的性質(例えば位置と運動量)を同時に知ることには、精度の根本的限界がある。
1928年 ディラック理論・・・量子力学と特殊相対性理論のどちらとも整合性のある理論
→電子にはパートナーとなる陽電子(反物質)がある。
1929年 宇宙膨張(銀河の赤方遷移)の発見(エドウィン・パウエル・ハッブル)
1932年 陽電子(反物質)の発見
1934年 フリッツ・ツビッキーが暗黒物質を提唱 [6]
1948年-ビッグバン・モデル(ガモフ)[7]
-量子電磁力学(Quantum electrodynamics, QED)[電磁気力]
・電子を始めとする荷電粒子間に働く電磁相互作用を光子という粒子の受け渡しにより説明した。
1957年 ブライス・デウィットが多世界解釈を提唱。
1960年 フリーマン・ダイソンがダイソン球を提唱
1964年-ピーター・ヒッグスが質量の生成に関する理論を提唱した。[8]
-宇宙マイクロ波背景放射[7]の発見
1968年 ワインバーグ=サラム理論[9] [電磁気力+弱い力]
1970年 ペンローズとホーキングの共著論文
:一般相対論が正しく、かつ宇宙が、われわれが現に観測しているのと同じ程度の物質を含んでさえいれば、宇宙のごく初期にはビッグバン特異点があったはずだということを最終的に証明した。
・特異点では、量子力学が扱う小さな尺度の効果が無視できなくなる。
・しかし、量子効果を考慮に入れると特異点は消え去る。・・・?
1970年代
・宇宙の始まりに存在したのは唯1つの力だけで、その後、電磁気力、弱い力、強い力、重力の四つに分かれたという考え方から、これら四つの力を一つの形で表して統一しようとしている。
○標準理論( Standard Model, SM) [電磁気力+弱い力(+強い力)] [9]
○大統一理論(Grand unification theory or Grand unified theory、GUT)[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力] [10]
1970年代後半 量子色力学 [9]
1980年代 素粒子論的宇宙論 [10]
1981年 インフレーション理論 [11]
1984年 超弦理論(Superstring theory 1984) [12] [電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力]
1986年~ ループ量子重力理論 [13]
1995年 M理論[電磁気力+弱い力+強い力+重力] [14]
1998年 -マイケル・ターナー 暗黒エネルギーという言葉を作る。[6]
-宇宙の加速膨張を観測(ブライアン・シュミット)
2016年 スタジオ・グーダ! 暗黒物質の構造を提案 [15]
【参 照】
1. No.14 相対性理論
2. No.13 ニュートン力学
3. No.80 ブラックホール
4. No.29 重力波
5. No.16 不確定性原理
6. No.9 暗黒物質と暗黒エネルギー
7. No.18 ビッグバン・モデル
8. No.23 ヒッグス場/ヒッグス粒子
9. No.19 標準理論(標準モデル)
10. No.21 素粒子論的宇宙論
11. No.21-2 インフレーション理論
12. No.24 超弦理論
13. No.26 ループ量子重力理論
14. No.25 M理論
15. No.86-4-2 暗黒物質の構造
【更新履歴】
20170416 宇宙のイメージの追加
20170515 No.32-1 分かっていること の追加
20171030 No.32-3 フリーマン・ダイソンの言葉の追加
31 Entanglement Entropy #gravity #universe #QuantumTheory #SuperStringTheory
○ Quantum Entanglement Entropy(EE):Number of quantum entanglements. An indicator of the quantification of quantum entanglement. = Number of EPR pair (EPR: Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen)
○ It is very difficult to calculate the entropy of quantum with quantum field theory, but in Anti de Sitter space(Ads), like a holography, It can be replaced by calculation of surface area of a bubble (like a black hole with the smallest surface area). :Ryu-Takayanagi formula(Holographic Entanglement Entropy Formula 2006) [1]
※Anti de Sitter space(Ads):One of the spaces where the curvature is negative and constant
= Universe with negative cosmic constant Λ (dark energy)
⇔de Sitter space(dS) (Positive curvature)
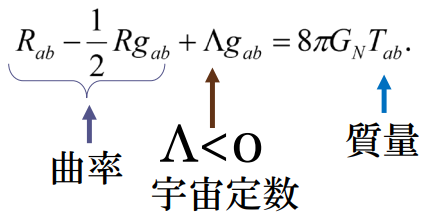
曲率:curvature, 宇宙定数:cosmic constant Λ, 質量:mass [2]
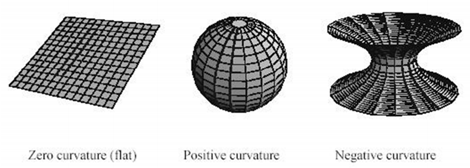
Figure:Curvature [3]
• A major feature of AdS is to be able to cover infinite space in a finite area.
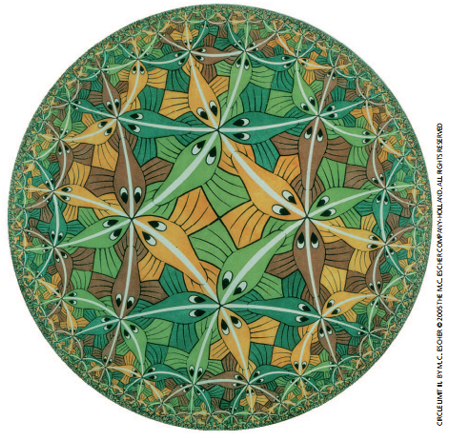

Firure:Escher's picture: It is close to the image which projected Anti de Sitter space on the plane.
• Although de Sitter space universe (Λ> 0) is close to the real universe, its holographic principle has not been elucidated. [4]
○Ryu-Takayanagi formula:Holographic Entanglement Entropy Formula (2006)
• They revealed that holographic principle is related to quantum entanglement.
• Calculation of the entropy of quantum entanglement in quantum field theory can be replaced with calculation of the surface area of bubble (shaped to minimize the surface area) generated in AdS. [5]
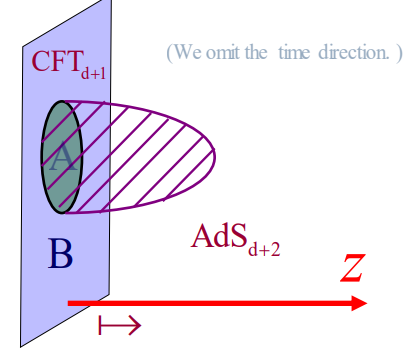
Figure:Thinking of the minimal aspect extending from the interface to the inside of the AdS space, calculating its area and dividing it by 4 times the Newton's constant of gravity theory is equivalent to entanglement entropy. [6]
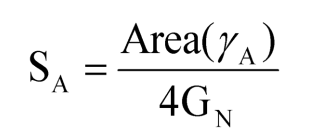
※Ryu-Takayanagi formula:Holographic Entanglement Entropy Formula
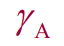
is the minimal area surface
・Generalization of Bekenstein-Hawking entropy formula.
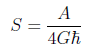
※Bekenstein-Hawking entropy [7]
○In Ryu-Takayanagi formula, one bit of quantum entanglement is present per planck area (1 square planck length).
※Planck length
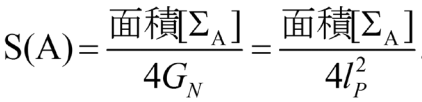
○Task:It is necessary to elucidate the quantum entanglement in de Sitter space.
○Application of quantum entangy entropy:
・Entangy entropy (EE) is helpful for understanding s of various (quantum) gravity phenomena such as black hole formations, singularities etc. [5]
・In certain substances, controlling interatomic distances and temperatures leads to the transition to "strange metal" (anomalous metallic phase), which has different electrical characteristics (superconductivity) from ordinary metals, It is caused by becoming quantum entangled state as a whole (rapid increase of quantum entanglement entropy).
【Refereces】
1. Ryu-Takayanagi Conjecture - Wikipedia
2. T. Takayanagi" Front line of super string theory:Is the universe created from qubits?“ 20170524(Japanese)
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~tadashi.takayanagi/JAXA17.pdf
3. 中村 真“非専門家のためのAdS/CFT対応入門” 20111214 (Japanese)
http://quattro.phys.sci.kobe-u.ac.jp/dmrg/Kyoto2011/Proc/Nakamura.pdf
4. 高柳 匡"超ひも理論の最前線:宇宙は量子ビットから創られているのか?“ 20170524 (Japanese)
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~tadashi.takayanagi/JAXA17.pdf
5. Tadashi Takayanagi” Entanglement Entropy and AdS/CFT” 2012
http://www2.yukawa.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~tadashi.takayanagi/CERNEE.pdf
6. Tadashi Takayanagi” Recent Developments in (Holographic) Entanglement Entropy” 2012
http://people.physik.hu-berlin.de/~ahoop/takayanagi.pdf
7. No.27-2 Thermodynamics and the Laws of Newton
【Chnge log】
20180117 Newly posted