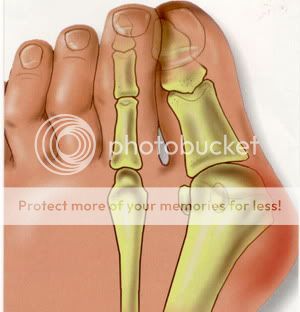
 Bunions are a common problem that most people experience as a bony protuberance at the base of the big toe. A bunion, however, is more complicated than simply a bump on the foot. When a patient has a bunion, the big toe angles in toward the other toes, a condition called hallux valgus. Bunions are most common in women, and the cause is most often unsuitable footwear.
Bunions are a common problem that most people experience as a bony protuberance at the base of the big toe. A bunion, however, is more complicated than simply a bump on the foot. When a patient has a bunion, the big toe angles in toward the other toes, a condition called hallux valgus. Bunions are most common in women, and the cause is most often unsuitable footwear. Causes
Bunions can be caused by improper footwear. Genetics. Foot injuries. Congenital deformities. Medical conditions such as arthritis. Stress on feet. Bunions are mainly caused by genetics. The bunion itself is not inherited, but the person?s hereditary foot type and gait pattern makes them more prone to developing bunions.You can also begin to develop bunionsby wearing shoes that are too tight or too small. When you wear shoes of this nature, your toes are squeezed together. Bunions are not caused by crowding of the toes, but wearing tight shoes can worsen the condition and cause symptoms to appear sooner. Some people are born with birth defects that put them at higher risk for developing bunions.
Symptoms
Symptoms include redness, swelling and pain which may be present along the inside margin of the foot. The patients feet may become too wide to fit into their normal size shoes and moderate to severe discomfort may occur when the patient is wearing tight shoes. A "hammer toe" may occur at the 2nd toe. This is when the toe contracts and presses on the shoe. Subsequently, this may cause a corn on top of the 2nd toe.
Diagnosis
When an x-ray of a bunion is taken, there is usually angulation between the first metatarsal bone and the bones of the big toe. There may also be angulation between the first and second metatarsal bones. These angular irregularities are the essence of most bunions. In general, surgery for bunions aims to correct such angular deformities.
Non Surgical Treatment
There is no way to eliminate existing bunions except to have them surgically removed. There are nonsurgical measures you can take to alleviate the pain and prevent your bunions from increasing in severity, and for that reason it's important to see your doctor before they become a serious problem. The more extensive your bunions are, the less effective nonsurgical treatments are. On the other hand, most bunions can be dealt with without surgery through wearing roomier, low-heel shoes, padding and taping your feet, using medications for pain control, going to physical therapy to relieve inflammation and wearing orthotics in your shoes to correct mechanical problems. Bunions that are not causing pain generally aren't appropriate for surgery. Roomier shoes. You should seek out shoes that conform to the shape of your feet as much as possible and provide plenty of room in the toe box, ensuring that your toes are not pinched or squeezed. You should make sure that, while standing, there is a half inch of space for your longest toe at the end of each shoe. Make sure the ball of your foot fits comfortably in the widest part of the shoe. Feet normally swell during the course of the day, so shop for shoes at the end of the day, when your feet are at their largest. Don't be vain about your shoe size, sizes vary by brand, so concentrate on making certain your shoes are comfortable. Remember that your two feet are very likely to be different sizes and fit your shoe size to the larger foot. Low-heel shoes. High heels shift all your body weight onto your toes, increasing the pressure on your toes and their joints tremendously. Instead, wear shoes with low (less than two inches) or flat heels that fit your foot comfortably. Padding and Taping. Padding the bunion can minimize pain and allow you to walk more normally. Specially designed pads for this are available at most drugstores. Taping your foot can reduce stress and pain in it by helping it stay in a more normal position. Medication. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and ibuprofen can help deal with pain and inflammation caused by your bunion. Cortisone injections may be prescribed for the same purpose. If your bunion is a consequence of arthritis in the MTP joint, your physician may prescribe medications for that. Physical Therapy. Ultrasound treatments and whirlpool baths can help reduce pain and inflammation in bunions and related tissues. Orthotics are shoe inserts that can help correct mechanical foot-motion problems to reduce pain and prevent worsening of your bunion. Other measures. Icing and elevating your foot when your bunion is painful may help. Having your shoes stretched at a shoe repair shop may help also.
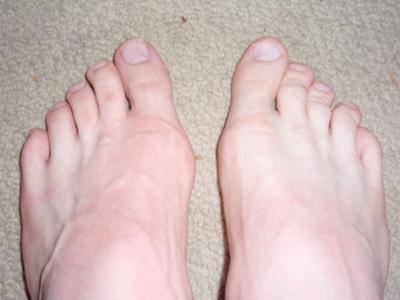
Surgical Treatment
Some sufferers choose to have the bunion surgically removed. This should always be a last resort as all surgeries carry risks. There are several types of surgical procedures to remove bunions and before deciding, you should speak to your surgeon at length about the facts and risks associated with surgery, including the recovery time and success rate of the operation to be done. Please note that if you have a surgical procedure and then return to your high heels and narrow-toed shoes, the bunion is likely to reoccur.